data_color: Perform data cell colorization
Description
It's possible to add color to data cells according to their values with the
data_color() function. There is a multitude of ways to perform data cell
colorizing here:
targeting: we can constrain which columns and rows should receive the colorization treatment (through the
columnsandrowsarguments)direction: ordinarily we perform coloring in a column-wise fashion but there is the option to color data cells in a row-wise manner (this is controlled by the
directionargument)coloring method:
data_color()automatically computes colors based on the column type but you can choose a specific methodology (e.g., with bins or quantiles) and the function will generate colors accordingly; themethodargument controls this through keywords and other arguments act as inputs to specific methodscoloring function: a custom function can be supplied to the
fnargument for finer control over color evaluation with data; the color mappingcol_*()functions in the scales package can be used here or any function you might want to definecolor palettes: with
palettewe could supply a vector of colors, a virdis or RColorBrewer palette name, or, a palette from the paletteer packagevalue domain: we can either opt to have the range of values define the domain, or, specify one explicitly with the
domainargumentindirect color application: it's possible to compute colors from one column and apply them to one or more different columns; we can even perform a color mapping from multiple source columns to the same multiple of target columns
color application: with the
apply_toargument, there's an option for whether to apply the cell-specific colors to the cell background or the cell texttext autocoloring: if colorizing the cell background,
data_color()will automatically recolor the foreground text to provide the best contrast (can be deactivated withautocolor_text = FALSE)
The data_color() function won't fail with the default options used, but
that won't typically provide you the type of colorization you really need.
You can however safely iterate through a collection of different options
without running into too many errors.
Usage
data_color(
data,
columns = everything(),
rows = everything(),
direction = c("column", "row"),
target_columns = NULL,
method = c("auto", "numeric", "bin", "quantile", "factor"),
palette = NULL,
domain = NULL,
bins = 8,
quantiles = 4,
levels = NULL,
ordered = FALSE,
na_color = NULL,
alpha = NULL,
reverse = FALSE,
fn = NULL,
apply_to = c("fill", "text"),
autocolor_text = TRUE,
contrast_algo = c("apca", "wcag"),
colors = NULL
)Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Arguments
- data
A table object that is created using the
gt()function.- columns, rows
The columns and rows to which cell data color operations are constrained.
- direction
Should the color computations be performed column-wise or row-wise? By default this is set with the
"column"keyword and colors will be applied down columns. The alternative option with the"row"keyword ensures that the color mapping works across rows.- target_columns
For indirect column coloring treatments, we can supply the columns that will receive the styling. The necessary precondition is that we must use
direction = "column". Ifcolumnsresolves to a single column then we may use one or more columns intarget_columns. If on the other handcolumnsresolves to multiple columns, thentarget_columnsmust resolve to the same multiple.- method
A method for computing color based on the data within body cells. Can be
"auto"(the default),"numeric","bin","quantile", or"factor". The"auto"method will automatically choose the"numeric"method for numerical input data or the"factor"method for any non-numeric inputs.- palette
A vector of color names, the name of an RColorBrewer palette, the name of a viridis palette, or a discrete palette accessible from the paletteer package using the
<package>::<palette>syntax (e.g.,"wesanderson::IsleofDogs1"). If providing a vector of colors as a palette, each color value provided must either be a color name (Only R/X11 color names or CSS 3.0 color names) or a hexadecimal string in the form of"#RRGGBB"or"#RRGGBBAA". If nothing is provided here, the default R color palette is used (i.e., the colors frompalette()).- domain
The possible values that can be mapped. For the
"numeric"and"bin"methods, this can be a numeric range specified with a length of two vector. Representative numeric data is needed for the"quantile"method and categorical data must be used for the"factor"method. IfNULL(the default value), the values in each column or row (depending ondirection) value will represent the domain.- bins
For
method = "bin"this can either be a numeric vector of two or more unique cut points, or, a single numeric value (greater than or equal to2) giving the number of intervals into which the domain values are to be cut. By default, this is8.- quantiles
For
method = "quantile"this is the number of equal-size quantiles to use. By default, this is set to4.- levels
For
method = "factor"this allows for an alternate way of specifying levels. If anything is provided here then any value supplied todomainwill be ignored. This should be a character vector of unique values.- ordered
For
method = "factor", setting this toTRUEmeans that the vector supplied todomainwill be treated as being in the correct order if that vector needs to be coerced to a factor. By default, this isFALSE.- na_color
The color to use for missing values. By default (with
na_color = NULL) gray,"#808080", will be used.- alpha
An optional, fixed alpha transparency value that will be applied to all of the
colorsprovided (regardless of whether a color palette was directly supplied or generated through a color mapping function).- reverse
Should the colors computed operate in reverse order? If
TRUEthen colors that normally change from red to blue will change in the opposite direction. By default, this isFALSE.- fn
A color-mapping function. The function should be able to take a vector of data values as input and return an equal-length vector of color values. The
col_*()functions provided in the scales package (i.e.,scales::col_numeric(),scales::col_bin(), andscales::col_factor()) can be invoked here with options, as those functions themselves return a color-mapping function.- apply_to
Which style element should the colors be applied to? Options include the cell background (the default, given as
"fill") or the cell text ("text").- autocolor_text
An option to let gt modify the coloring of text within cells undergoing background coloring. This will result in better text-to-background color contrast. By default, this is set to
TRUE.- contrast_algo
The color contrast algorithm to use when
autocolor_text = TRUE. By default this is"apca"(Accessible Perceptual Contrast Algorithm) and the alternative to this is"wcag"(Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).- colors
Deprecated. Use the
fnargument instead to provide a scales-based color-mapping function. If providing a palette, use thepaletteargument.
Targeting cells with <code>columns</code> and <code>rows</code>
Targeting of values is done through columns and additionally by rows (if
nothing is provided for rows then entire columns are selected). The
columns argument allows us to target a subset of cells contained in the
resolved columns. We say resolved because aside from declaring column names
in c() (with bare column names or names in quotes) we can use
tidyselect-style expressions. This can be as basic as supplying a select
helper like starts_with(), or, providing a more complex incantation like
where(~ is.numeric(.x) && max(.x, na.rm = TRUE) > 1E6)
which targets numeric columns that have a maximum value greater than
1,000,000 (excluding any NAs from consideration).
By default all columns and rows are selected (with the everything()
defaults). Cell values that are incompatible with a given coloring
function/method will be skipped over. One strategy is to color the bulk of
cell values with one formatting function and then constrain the columns for
later passes (the last coloring done to a cell is what you get in the final
output).
Once the columns are targeted, we may also target the rows within those
columns. This can be done in a variety of ways. If a stub is present, then we
potentially have row identifiers. Those can be used much like column names in
the columns-targeting scenario. We can use simpler tidyselect-style
expressions (the select helpers should work well here) and we can use quoted
row identifiers in c(). It's also possible to use row indices (e.g.,
c(3, 5, 6)) though these index values must correspond to the row numbers of
the input data (the indices won't necessarily match those of rearranged rows
if row groups are present). One more type of expression is possible, an
expression that takes column values (can involve any of the available columns
in the table) and returns a logical vector. This is nice if you want to base
formatting on values in the column or another column, or, you'd like to use a
more complex predicate expression.
Color computation methods
The data_color() function offers four distinct methods for computing color
based on cell data values. They are set by the method argument and the
options go by the keywords "numeric", "bin", "quantile", and
"factor". There are other arguments in data_color() that variously
support these methods (e.g., bins for the "bin" method, etc.). Here we'll
go through each method, providing a short explanation of what each one does
and which options are available.
"numeric"
The "numeric" method provides a simple linear mapping from continuous
numeric data to an interpolated palette. Internally, this uses the
scales::col_numeric() function. This method is suited for numeric data cell
values and can make use of a supplied domain value, in the form of a
two-element numeric vector describing the range of values, if provided.
"bin"
The "bin" method provides a mapping of continuous numeric data to
value-based bins. Internally, this uses the scales::col_bin() function
which itself uses base::cut(). As with the "numeric" method, "bin" is
meant for numeric data cell values. The use of a domain value is supported
with this method. The bins argument in data_color() is specific to this
method, offering the ability to: (1) specify the number of bins, or (2)
provide a vector of cut points.
"quantile"
The "quantile" method provides a mapping of continuous numeric data to
quantiles. Internally, this uses the scales::col_quantile() function which
itself uses stats::quantile(). Input data cell values should be numeric, as
with the "numeric" and "bin" methods. A numeric domain value is
supported with this method. The quantiles argument in data_color()
controls the number of equal-size quantiles to use.
"factor"
The "factor" method provides a mapping of factors to colors. With discrete
palettes, color interpolation is used when the number of factors does not
match the number of colors in the palette. Internally, this uses the
scales::col_factor() function. Input data cell values can be of any type
(i.e., factor, character, numeric values, and more are supported). The
optional input to domain should take the form of categorical data. The
levels and ordered arguments in data_color() support this method.
Color palette access from <strong>RColorBrewer</strong> and <strong>viridis</strong>
All palettes from the RColorBrewer package and select palettes from
viridis can be accessed by providing the palette name in palette.
RColorBrewer has 35 available palettes:
| Palette Name | Colors | Category | Colorblind Friendly | |
| 1 | "BrBG" | 11 | Diverging | Yes |
| 2 | "PiYG" | 11 | Diverging | Yes |
| 3 | "PRGn" | 11 | Diverging | Yes |
| 4 | "PuOr" | 11 | Diverging | Yes |
| 5 | "RdBu" | 11 | Diverging | Yes |
| 6 | "RdYlBu" | 11 | Diverging | Yes |
| 7 | "RdGy" | 11 | Diverging | No |
| 8 | "RdYlGn" | 11 | Diverging | No |
| 9 | "Spectral" | 11 | Diverging | No |
| 10 | "Dark2" | 8 | Qualitative | Yes |
| 11 | "Paired" | 12 | Qualitative | Yes |
| 12 | "Set1" | 9 | Qualitative | No |
| 13 | "Set2" | 8 | Qualitative | Yes |
| 14 | "Set3" | 12 | Qualitative | No |
| 15 | "Accent" | 8 | Qualitative | No |
| 16 | "Pastel1" | 9 | Qualitative | No |
| 17 | "Pastel2" | 8 | Qualitative | No |
| 18 | "Blues" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 19 | "BuGn" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 20 | "BuPu" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 21 | "GnBu" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 22 | "Greens" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 23 | "Greys" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 24 | "Oranges" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 25 | "OrRd" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 26 | "PuBu" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 27 | "PuBuGn" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 28 | "PuRd" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 29 | "Purples" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 30 | "RdPu" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 31 | "Reds" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 32 | "YlGn" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 33 | "YlGnBu" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 34 | "YlOrBr" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
| 35 | "YlOrRd" | 9 | Sequential | Yes |
We can access four colorblind-friendly palettes from viridis:
"viridis", "magma", "plasma", and "inferno". Simply provide any one
of those names to palette.
Color palette access from <strong>paletteer</strong>
Choosing the right color palette can often be difficult because it's both
hard to discover suitable palettes and then obtain the vector of colors. To
make this process easier we can elect to use the paletteer package,
which makes a wide range of palettes from various R packages readily
available. The info_paletteer() information table allows us to easily
inspect all of the discrete color palettes available in paletteer. We
only then need to specify the palette and associated package using the
<package>::<palette> syntax (e.g., "tvthemes::Stannis") for
the palette argument.
A requirement for using paletteer in this way is that the package must be
installed (gt doesn't import paletteer currently). This can be easily
done with install.packages("paletteer"). Not having this package installed
with result in an error when using the <package>::<palette> syntax in
palette.
Foreground text and background fill
By default, gt will choose the ideal text color (for maximal contrast)
when colorizing the background of data cells. This option can be disabled by
setting autocolor_text to FALSE. The contrast_algo argument lets us
choose between two color contrast algorithms: "apca" (Accessible
Perceptual Contrast Algorithm, the default algo) and "wcag" (Web Content
Accessibility Guidelines).
Examples
The data_color() function can be used without any supplied arguments to
colorize a gt table. Let's do this with the exibble dataset:
exibble |>
gt() |>
data_color()
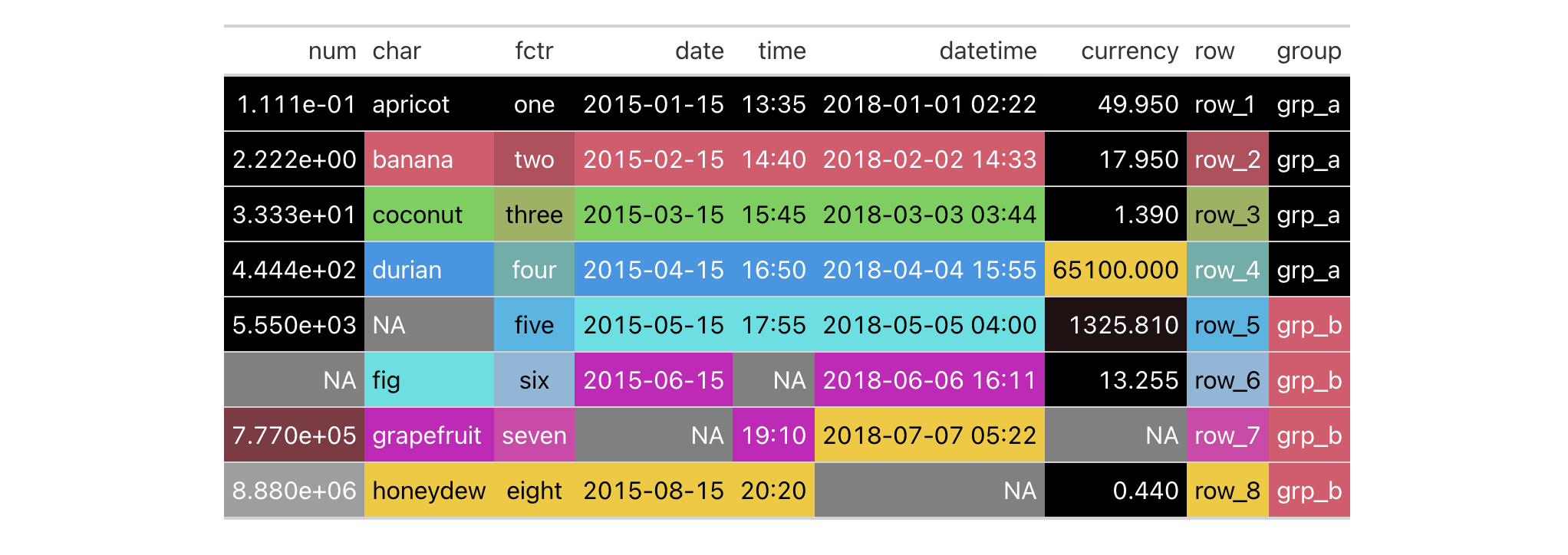
What's happened is that data_color() applies background colors to all cells
of every column with the default palette in R (accessed through palette()).
The default method for applying color is "auto", where numeric values will
use the "numeric" method and character or factor values will use the
"factor" method. The text color will be undergo modification automatically
to maximize contrast (since autocolor_text is TRUE by default).
You can use any of the available method keywords and gt will only apply
color to the compatible values. Let's use the "numeric" method and supply
palette values of "red" and "green".
exibble |>
gt() |>
data_color(
method = "numeric",
palette = c("red", "green")
)
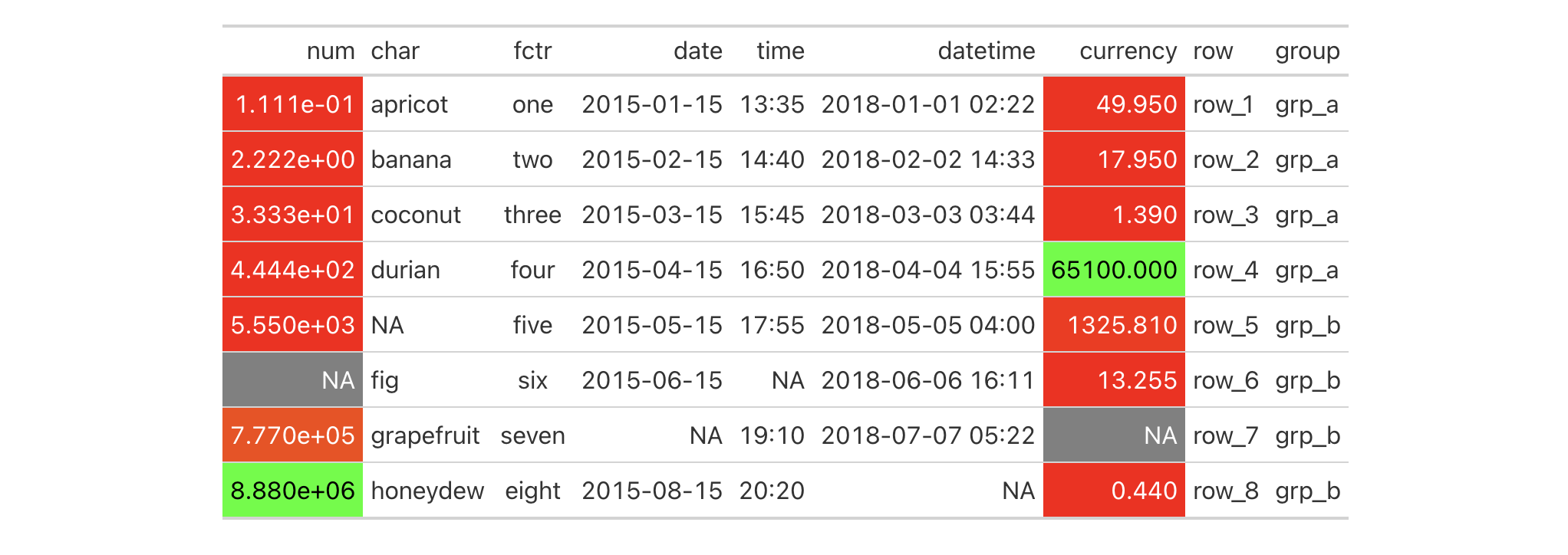
With those options in place we see that only the numeric columns num and
currency received color treatments. Moreover, the palette colors were
mapped to the lower and upper limits of the data in each column; interpolated
colors were used for the values in between the numeric limits of the two
columns.
We can constrain the cells to which coloring will be applied with the
columns and rows arguments. Further to this, we can manually set the
limits of the data with the domain argument (which is preferable in most
cases). Here, the domain will be set as domain = c(0, 50).
exibble |>
gt() |>
data_color(
columns = currency,
rows = currency < 50,
method = "numeric",
palette = c("red", "green"),
domain = c(0, 50)
)

We can use any of the palettes available in the RColorBrewer and
viridis packages. Let's make a new gt table from a subset of the
countrypops dataset. Then, through data_color(), we'll apply coloring
to the population column with the "numeric" method, use a domain between
2.5 and 3.4 million, and specify palette = "viridis".
countrypops |>
dplyr::filter(country_name == "Mongolia") |>
dplyr::select(-contains("code")) |>
tail(10) |>
gt() |>
data_color(
columns = population,
method = "numeric",
palette = "viridis",
domain = c(2.5E6, 3.4E6)
)

We can alternatively use the fn argument for supplying the scales-based
function scales::col_numeric(). That function call will itself return a
function (which is what the fn argument actually requires) that takes a
vector of numeric values and returns color values. Here is the more complex
version of the code that returns the same table as in the previous example.
countrypops |>
dplyr::filter(country_name == "Mongolia") |>
dplyr::select(-contains("code")) |>
tail(10) |>
gt() |>
data_color(
columns = population,
fn = scales::col_numeric(
palette = "viridis",
domain = c(2.5E6, 3.4E6)
)
)

Using your own function in fn can be very useful if you want to make use of
specialized arguments in the scales col_*() functions. You could even
supply your own specialized function for performing complex colorizing
treatments!
The data_color() function has a way to apply colorization indirectly to
other columns. That is, you can apply colors to a column different from the
one used to generate those specific colors. The trick is to use the
target_columns argument. Let's do this with a more complete
countrypops-based table example.
countrypops |>
dplyr::filter(country_code_3 %in% c("FRA", "GBR")) |>
dplyr::filter(year %% 10 == 0) |>
dplyr::select(-contains("code")) |>
dplyr::mutate(color = "") |>
gt(groupname_col = "country_name") |>
fmt_integer(columns = population) |>
data_color(
columns = population,
target_columns = color,
method = "numeric",
palette = "viridis",
domain = c(4E7, 7E7)
) |>
cols_label(
year = "",
population = "Population",
color = ""
) |>
opt_vertical_padding(scale = 0.65)

When specifying a single column in columns we can use as many
target_columns values as we want. Let's make another countrypops-based
table where we map the generated colors from the year column to all columns
in the table. This time, the palette used is "inferno" (also from the
viridis package).
countrypops |>
dplyr::filter(country_code_3 %in% c("FRA", "GBR", "ITA")) |>
dplyr::select(-contains("code")) |>
dplyr::filter(year %% 5 == 0) |>
tidyr::pivot_wider(
names_from = "country_name",
values_from = "population"
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_integer(columns = c(everything(), -year)) |>
cols_width(
year ~ px(80),
everything() ~ px(160)
) |>
opt_all_caps() |>
opt_vertical_padding(scale = 0.75) |>
opt_horizontal_padding(scale = 3) |>
data_color(
columns = year,
target_columns = everything(),
palette = "inferno"
) |>
tab_options(
table_body.hlines.style = "none",
column_labels.border.top.color = "black",
column_labels.border.bottom.color = "black",
table_body.border.bottom.color = "black"
)

Now, it's time to use pizzaplace to create a gt table. The color
palette to be used is the "ggsci::red_material" one (it's in the ggsci
R package but also obtainable from the the paletteer package).
Colorization will be applied to the to the sold and income columns. We
don't have to specify those in columns because those are the only columns
in the table. Also, the domain is not set here. We'll use the bounds of the
available data in each column.
pizzaplace |>
dplyr::group_by(type, size) |>
dplyr::summarize(
sold = dplyr::n(),
income = sum(price),
.groups = "drop_last"
) |>
dplyr::group_by(type) |>
dplyr::mutate(f_sold = sold / sum(sold)) |>
dplyr::mutate(size = factor(
size, levels = c("S", "M", "L", "XL", "XXL"))
) |>
dplyr::arrange(type, size) |>
gt(
rowname_col = "size",
groupname_col = "type"
) |>
fmt_percent(
columns = f_sold,
decimals = 1
) |>
cols_merge(
columns = c(size, f_sold),
pattern = "{1} ({2})"
) |>
cols_align(align = "left", columns = stub()) |>
data_color(
method = "numeric",
palette = "ggsci::red_material"
)

Colorization can occur in a row-wise manner. The key to making that happen is
by using direction = "row". Let's use the sza dataset to make a gt
table. Then, color will be applied to values across each 'month' of data in
that table. This is useful when not setting a domain as the bounds of each
row will be captured, coloring each cell with values relative to the range.
The palette is "PuOr" from the RColorBrewer package (only the name
here is required).
sza |>
dplyr::filter(latitude == 20 & tst <= "1200") |>
dplyr::select(-latitude) |>
dplyr::filter(!is.na(sza)) |>
tidyr::spread(key = "tst", value = sza) |>
gt(rowname_col = "month") |>
sub_missing(missing_text = "") |>
data_color(
direction = "row",
palette = "PuOr",
na_color = "white"
)

Notice that na_color = "white" was used, and this avoids the appearance of
gray cells for the missing values (we also removed the "NA" text with
sub_missing(), opting for empty strings).
Function ID
3-30
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other data formatting functions:
fmt_auto(),
fmt_bins(),
fmt_bytes(),
fmt_currency(),
fmt_datetime(),
fmt_date(),
fmt_duration(),
fmt_engineering(),
fmt_flag(),
fmt_fraction(),
fmt_image(),
fmt_index(),
fmt_integer(),
fmt_markdown(),
fmt_number(),
fmt_partsper(),
fmt_passthrough(),
fmt_percent(),
fmt_roman(),
fmt_scientific(),
fmt_spelled_num(),
fmt_time(),
fmt_url(),
fmt(),
sub_large_vals(),
sub_missing(),
sub_small_vals(),
sub_values(),
sub_zero()